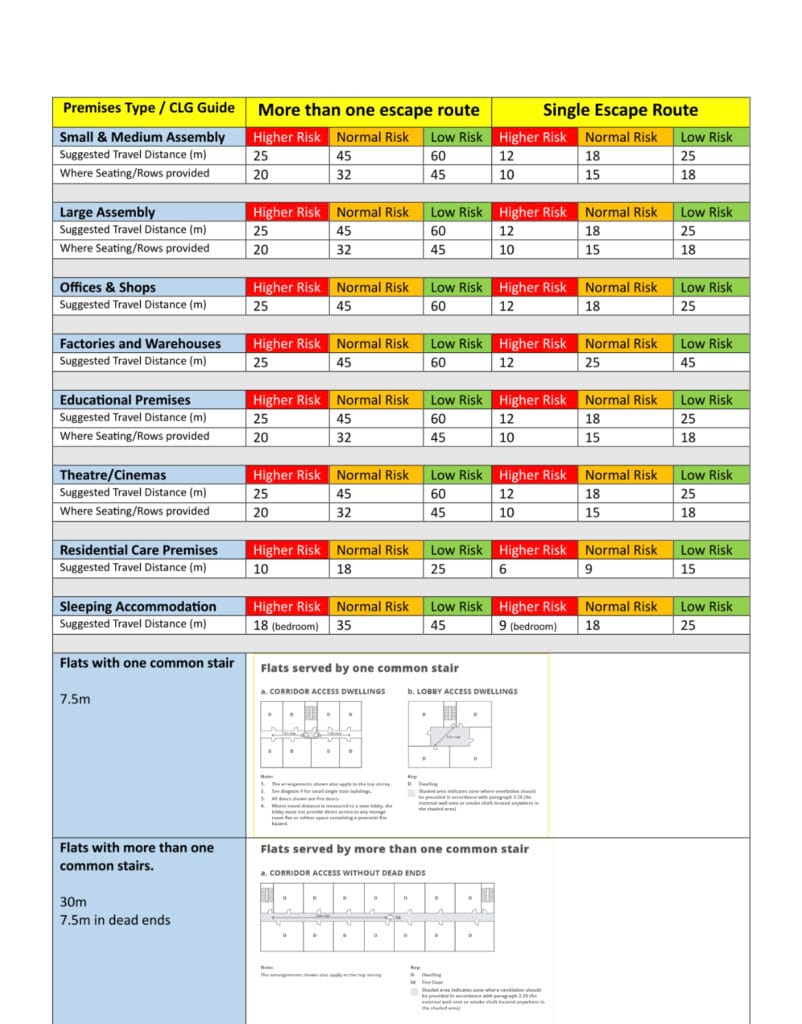
Understanding Permitted Travel Distances for Fire Safety in the UK
Fire safety is a paramount concern in building design and occupancy, particularly in the UK. Here, regulations dictate strict guidelines to ensure the safety of occupants in the event of a fire. One crucial aspect of fire safety is understanding permitted travel distances. These play a vital role in the effectiveness of escape routes and the overall safety strategy of a building.
Permitted Travel Distances?
Permitted travel distances refer to the maximum distance that occupants must travel to reach a place of safety. This includes an exit or a designated assembly point during an emergency evacuation. These distances vary depending on several factors. These include the type of building, its use, the number of occupants, and the presence of fire safety measures such as fire doors, alarms, and sprinkler systems.
Key Regulations and Guidelines
In the UK, the primary legislation governing fire safety is the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005. This order places the responsibility for fire safety on the ‘responsible person’—typically the owner or manager of a building. The order emphasises the need for a comprehensive fire risk assessment, which includes evaluating travel distances.
Here are some key considerations regarding permitted travel distances:
1. **General Guidelines**:
– For most buildings, the maximum permitted travel distance to a final exit must not exceed 18 meters (approximately 59 feet) when there is no sprinkler system installed.
– If a building is equipped with a sprinkler system, this distance will increase to 45 meters (approximately 148 feet).
2. **Special Considerations for High-Risk Occupancies**:
– Buildings with a higher risk of fire, such as factories or warehouses, may have stricter guidelines. For these types of buildings, travel distances are limited to 15 meters without sprinklers.
3. **Single vs. Multiple Exits**:
– In buildings with multiple exits, the distances can be adjusted based on the availability and location of these exits. The aim is to ensure that no occupant is more than the permitted distance from an exit.
4. **Use of Fire Compartmentation**:
– Fire compartmentation involves creating fire-resisting structures within a building to slow down the spread of fire and smoke. This can influence the permitted travel distances. Effective compartmentation may allow for longer distances to exits.
5. **Consideration for Vulnerable Occupants**:
– Special considerations must be made for buildings that house vulnerable populations, such as care homes or schools. In these cases, shorter permitted travel distances may be necessary to ensure safety.
Importance of Compliance
Adhering to permitted travel distances is not just about meeting legal requirements; it is crucial for the safety of all building occupants. Properly designed escape routes can reduce evacuation times, lower the risk of injury, and ultimately save lives. Regular training and drills must also be conducted to familiarise occupants with evacuation routes and procedures.
Conclusion
Understanding permitted travel distances is essential for effective fire safety management in the UK. By complying with regulations and conducting thorough fire risk assessments, responsible persons can create safer environments for everyone. Remember, safety is a shared responsibility—let’s work together to ensure we are all prepared in the event of a fire.
